Blog Posts Tagged Technical Content
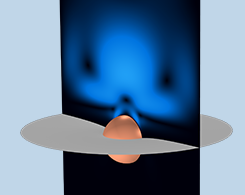
Modeling a Sphere Falling on a Water Surface
Get the theory behind a quintessential CFD problem, the oscillating motion of a buoyant sphere, as well as step-by-step instructions for modeling it in COMSOL Multiphysics®.
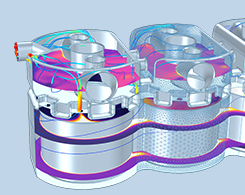
Calculating Thermodynamic Properties for Liquids and Gases
The Chemical Reaction Engineering Module includes a built-in database of over a dozen thermodynamic properties, making it easier to set up your transport and reaction models. Details here.
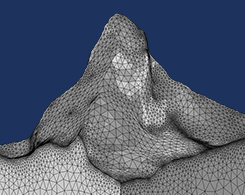
How to Build Geometries from Elevation Data to Model Irregular Shapes
Say you want to build an irregular geometry of a mountain. You can do so by creating a surface of an irregular shape based on elevation data stored formats such as text, image, or DEM files.
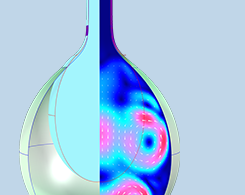
How to Model Fluid-Structure Interaction in a Water Balloon
They’re not just for playing games in the backyard: Water balloons are also an example of fluid–structure interaction in a nonlinear elastic material. Learn how to model this effect…
What Happens If I Use 2 Different Unit Systems in 1 Simulation?
Using 2 different unit systems for 1 project has led to historical disasters. Fortunately, you can use different unit systems in your simulation without issues by using the COMSOL® software.
How to Model Optical Anisotropic Media with COMSOL Multiphysics®
Erasmus Bartholinus first observed the optical effect of birefringence in 1669. Today, you can observe this effect with a specialized modeling approach for optical anisotropic media.
Should I Fillet the Geometry in My Electromagnetic Heating Analysis?
You want to analyze electromagnetic heating around sharp corners in your simulation. Do you round off the corners by adding a fillet? We go over cases where you should and shouldn’t do so.
How to Model Wet Chemical Etching in COMSOL Multiphysics®
Wet chemical etching was one of Rembrandt’s favorite methods for creating self-portraits. Now, it’s used by engineers to produce integrated circuits, MEMS devices, and pressure sensors.



