Scopri come la simulazione multifisica viene utilizzata per ricerca e sviluppo
In questa sezione troverete i lavori presentati alle Conferenze mondiali COMSOL. Le presentazioni descrivono ricerche e prodotti innovativi progettati con COMSOL Multiphysics da colleghi di tutto il mondo. I temi delle ricerche presentate abbracciano un'ampia gamma di settori produttivi e aree applicative, in ambito elettrico, meccanico, fluidodinamico e chimico. Lo strumento di Ricerca Rapida vi permetterà di trovare le presentazioni che si riferiscono all'area di vostro interesse.
Visualizza gli articoli presentati alla COMSOL Conference 2020
Although the cardiac arrest in pregnancy is a rare event it can have significant impact in terms of age of mother, mortality of unborn children and consequently long-term effect. One of the commonly used procedures in resuscitation is defibrillation. With recent advances in ... Per saperne di più
Characterization of particles has numerous applications in science and diagnostics. Recently, particle passage through constrained microchannels has been proposed to characterize particles based on their passage velocity. Nevertheless, there is no clear understanding of how the physics ... Per saperne di più
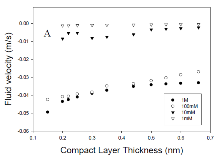
Interstitial fluid pressure (IFP) is elevated in tumors. Owing to this elevated IFP, the interstitial fluid velocity (IFV) is negligible throughout the tumor but significant near the tumor margin. Any therapeutic strategy that can lower IFP will improve drug convection within the tumor ... Per saperne di più
The radiation dose produced by an x-ray CT scanner to the patient is conventionally referenced to measurements performed by an ionization chamber in a phantom. On a fundamental level, the radiation absorbed dose, J/kg, can be determined directly by the temperature rise in the absorbing ... Per saperne di più
Whilst initially developed as a diagnostic aid to improve echogenicity in ultrasound imaging, gas-filled lipid microbubbles are now emerging as a next generation \'theranostic\' tool in the medical arena. Here, their therapeutic potential has now been realized through their unique ... Per saperne di più
This project utilizes the heat transfer module of the COMSOL Multiphysics environment to model the effects that an ohmic heating probe will have on neural tissue. The model quantifies the thermal impact of active components embedded on a neural micro probe by solving the Penne’s bioheat ... Per saperne di più
Electrofluidic transport through a single walled carbon nanotube (SWCNT) is enhanced by electroosmosis. Electroosmosis is made possible in these devices by the combination of a large slip length within SWCNTs and the interfacial potential at the solution/nanotube interface. A ... Per saperne di più
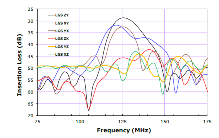
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) devices are commonly used as wireless filters, resonators, and sensors. The confinement of acoustic energy near the surface of a piezoelectric substrate in a SAW sensor makes it highly sensitive for discerning surface perturbation. As sensors, SAW devices have ... Per saperne di più
Singlet oxygen (1O2) is the major cytotoxic agent during photodynamic therapy (PDT). A previously developed model that incorporates the diffusion equation for the light transport in tissue and the macroscopic kinetic equations for the generation of the singlet oxygen, can be used to ... Per saperne di più
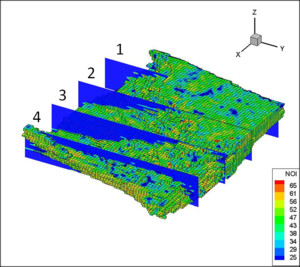
As in all tissues, mechanical forces in the aortic valve (AV) modulate the constituent cell population’s physiology and biosynthetic activity. While advances have been made toward the understanding of this complex multi-scale relationship, the specific role that and extracellular matrix ... Per saperne di più