La Galleria delle Applicazioni raccoglie un'ampia varietà di tutorial e di app dimostrative realizzati con COMSOL Multiphysics in diversi ambiti applicativi, inclusi quelli elettrico, meccanico, fluidico e chimico. E' possibile scaricare i file dei modelli e delle app demo pronti all'uso e le istruzioni step-by-step per costruirli, e utilizzarli come punto di partenza per le proprie simulazioni.
Lo strumento di Ricerca Rapida permette di trovare i modelli che si riferiscono alla propria area di interesse.
Si noti che molti degli esempi qui presentati sono accessibili anche tramite le Librerie delle Applicazioni incorporate nel software COMSOL Multiphysics® e disponibili dal menu File.
This model shows how to define a frequency-domain analysis of heat transfer. The 3-omega method uses the Cahill's equation to approximate the thermal conductivity of a sample from the measured temperature of a metal strip placed on top of it and subject to oscillating heating. The 2D ... Per saperne di più
The dispersion curves for a fluid-filled pipe with elastic walls are computed and compared with the analytical results for a pure elastic and an acoustic waveguide, respectively. Results show good agreement and also provide insight into the dynamics of the fluid-filled pipe at low and ... Per saperne di più
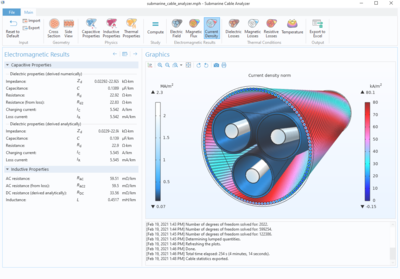
This application demonstrates how the Application Builder in the COMSOL Multiphysics® software can be used to make advanced cable modeling available to a general audience. At its core is a multiphysics model based on the technology introduced in the Cable Tutorial Series. The ... Per saperne di più
The model illustrate the technique to calculate the magnetic stiffness in a 3D geometry of a permanent magnet axial magnetic bearing. The Magnetic Fields physics is used to model the bearing and compute the magnetic forces. The Deformed Geometry and Sensitivity physics are used to ... Per saperne di più
The Dzhanibekov effect, also called the intermediate axis theorem or tennis racket theorem, describes the behavior of a rigid body with three distinct principal moments of inertia. This simulation app can be used to test the Dzhanibekov effect in three different geometries, including a ... Per saperne di più
In this example, a heat transfer model of a fiber composite's unit cell is analyzed with the Cell Periodicity feature. The homogenized thermal conductivity, density and heat capacity of a composite material are computed based on the individual properties of fiber and matrix. A comparison ... Per saperne di più
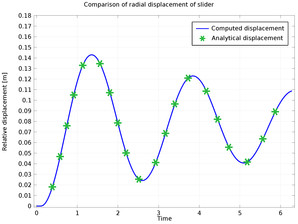
This model illustrates the modeling of slider motion caused by a base rotation. The motion of the slider is analyzed under various forces such as inertia force, centrifugal force, spring force and damping force. The prismatic joint, which is used to connect the two components, is spring ... Per saperne di più
Oscillating chemical reactions were long thought to simply not exist in homogeneous solution, and even the poster child, the Belousov–Zhabotinsky reaction, met such an initial skepticism, that even though it was discovered in 1951, it took almost 20 years for it to gain widespread fame. ... Per saperne di più
The model of 1D Dielectric Barrier Discharge (DBD) has been recomputed with the three different kinds of electron energy distribution functions (EEDFs): The Maxwellian function The Druyvesteyn function The computed EEDF based on the Boltzmann Equation, Two-Term Approximation ... Per saperne di più
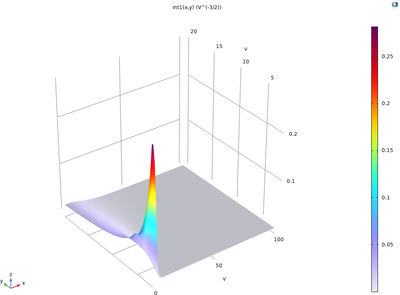
Say you would like to simulate a natural material or an arrangement of parts that have some known statistical distribution of dimensional variations. In such cases, you can create a random geometry based on these variations. This model file is an example that demonstrates how to create ... Per saperne di più